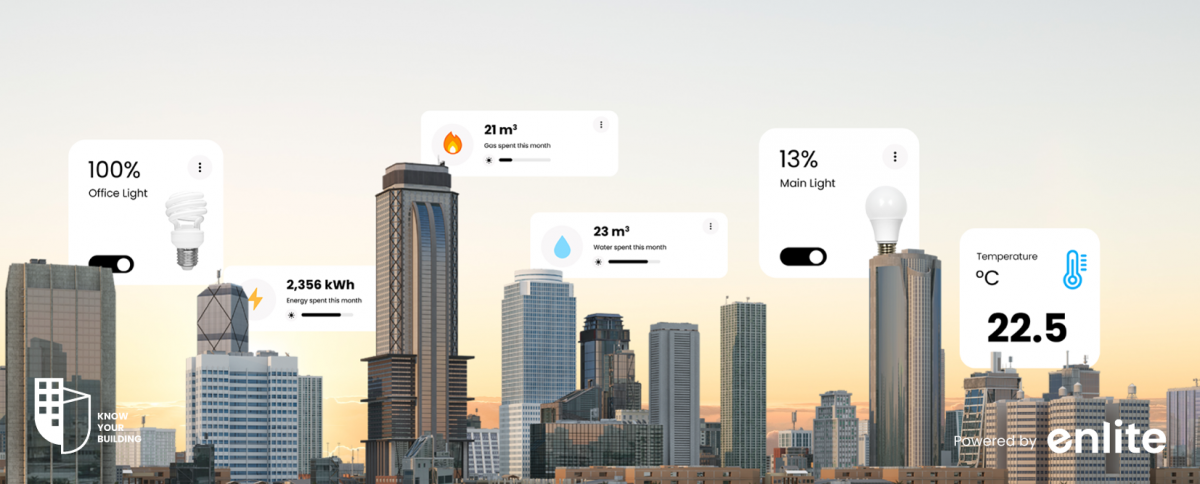
Introduction
Utilities, the lifeblood of any building, encompass the vital services and resources that keep it running smoothly. From electricity to water, heating to waste management, efficient utilities management is crucial for the well-being of both the environment and your wallet. This blog delves into the world of Utilities Monitoring in Buildings to highlight its importance, benefits, and best practices for optimal utilization.
Types of Building Utilities
Electricity: This utility provides power for lighting, appliances, heating and cooling systems, and various electrical devices within the building.
Water: Water utilities supply potable water for drinking, cooking, and sanitation purposes. Additionally, buildings may use non-potable water for activities like irrigation.
Gas: Natural gas is used for heating, cooking, and, in some cases, electricity generation. It’s a common utility for residential and commercial buildings.
Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC): This includes both heating and air conditioning systems, which help maintain a comfortable indoor environment. They can be powered by electricity or natural gas.
Sewage and Wastewater: Buildings require sewage systems to remove and process wastewater, ensuring sanitation and hygiene.
Waste Management: This utility involves the collection, removal, and disposal of solid waste and recycling materials generated within the building.
Telecommunications: In the modern age, buildings are equipped with utilities for internet, phone lines, and cable TV to facilitate communication and information exchange.
Security Systems: Building security systems include alarms, surveillance cameras, access control, and fire detection systems.
Lighting: Lighting utilities encompass the provision of artificial and natural light within the building. This includes electrical lighting and windows for natural lighting.
Elevators and Escalators: In multi-story buildings, elevators and escalators are essential for vertical transportation and accessibility.
Emergency Power: Emergency generators provide backup power in case of electrical outages, ensuring safety and continuity of operations.
Fire Suppression Systems: Fire protection utilities include sprinkler systems, fire extinguishers, and alarms to safeguard against fires.
Data and Communication: Data utilities involve cabling, networking, and data centers, which are crucial for businesses and institutions.
Waste Disposal and Recycling: Proper disposal and recycling systems are necessary to manage various types of waste generated within a building.
Stormwater Management: Stormwater utilities are essential to manage and divert rainwater to prevent flooding and erosion.
Plumbing and Sanitary Facilities: Plumbing utilities provide potable water supply and manage wastewater. Sanitary facilities include sinks, toilets, and showers.
Heating Oil or Propane: In some regions, heating oil or propane may be used as an alternative to natural gas for heating and appliances.
Advantages of Utilities Monitoring in Buildings
Monitoring utilities in buildings offers numerous advantages that impact not only the building itself but also its occupants, the environment, and the bottom line. Let’s explore these advantages in more detail:
Cost Reduction: One of the most immediate benefits of utilities monitoring in buildings is cost reduction. By tracking and analyzing utility consumption, building owners and managers can identify areas of excess usage, inefficiencies, and waste. This information allows for targeted cost-saving measures, such as optimizing heating and cooling systems, upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, and implementing energy-saving lighting solutions. Over time, these efforts can lead to substantial savings on utility bills.
Resource Savings: Efficient utilities monitoring helps conserve valuable resources such as electricity and water. This not only reduces operating costs but also contributes to the conservation of precious resources, which is vital for a sustainable future. For example, water monitoring can help identify and fix leaks, preventing water wastage, while electricity monitoring can lead to more efficient use of power.
Environmental Benefits: Sustainable building practices are increasingly important in today’s world. Efficient utilities monitoring supports environmental goals by reducing a building’s carbon footprint. Reduced energy consumption, water conservation, and waste management practices all have a positive impact on the environment. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote eco-friendly building practices.
Enhanced Comfort and Safety: Effective utilities monitoring can lead to improved comfort and safety for building occupants. For instance, optimized HVAC systems ensure consistent temperatures and air quality, creating a more pleasant and productive environment. Additionally, monitoring can identify safety hazards, such as electrical issues, gas leaks, or water damage, allowing for timely interventions to ensure occupant safety.
Compliance with Green Building Standards: Many building standards and certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or ENERGY STAR, require adherence to specific sustainability and energy efficiency criteria. Monitoring utilities is essential for demonstrating compliance with these standards, which can enhance a building’s reputation, marketability, and overall value.
Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring systems can also enable predictive maintenance, which helps identify and address potential issues before they become major problems. For example, predictive maintenance for HVAC systems can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure uninterrupted comfort for occupants.
Improved Building Performance: Efficient utilities management enhances the overall performance of a building. This includes better energy efficiency, more stable and comfortable indoor environments, and reduced downtime due to maintenance or unexpected utility-related issues. All of these contribute to the long-term value and functionality of the building.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Utilities monitoring provides valuable data that can inform strategic decision-making. With accurate and real-time data, building owners and managers can make informed choices about resource allocation, equipment upgrades, and sustainability initiatives. This data-driven approach ensures that investments are targeted to where they will have the most impact.
Occupant Satisfaction: Buildings with well-monitored utilities are more likely to provide a comfortable and safe environment for occupants. This, in turn, leads to increased occupant satisfaction and well-being. Satisfied occupants are more likely to stay longer in a building, reducing turnover and vacancy rates.
Competitive Advantage: In an increasingly sustainability-conscious world, buildings that prioritize utilities monitoring and efficient resource use gain a competitive advantage. Such buildings are attractive to environmentally conscious tenants, investors, and partners, enhancing the reputation and marketability of the property.
Future Trends in Building Utilities Monitoring
Predictive Analytics and AI: Predictive analytics and AI-driven solutions are being used to analyze historical data, predict resource usage patterns, and offer insights for proactively addressing issues, leading to significant cost savings and improved building performance.
Blockchain for Energy Management: Blockchain technology is transforming energy management by facilitating transparent and secure energy trading, automated billing, and decentralized energy generation, supporting sustainability and reducing energy losses.
Energy Storage and Microgrids: Energy storage solutions and microgrids are enhancing resilience and energy efficiency by storing excess energy, reducing peak demand, and integrating renewable energy sources to lower costs and environmental impact.
Energy and Water Efficiency Certification Programs: Certification programs like LEED and WELL increasingly incorporate rigorous utilities monitoring and data reporting requirements to drive sustainable practices and achieve higher ratings.
Occupant Engagement and Feedback: Occupant engagement platforms empower building users to monitor and adjust resource consumption, promoting energy-saving behaviors and contributing to sustainability efforts.
Grid-Interactive Buildings: Grid-interactive buildings participate in demand response programs and support grid stability, reducing energy costs during peak periods and potentially earning revenue from grid services.
Green Leases and Sustainability Agreements: Green leases and sustainability agreements between building owners and tenants create shared incentives for efficient utilities management, reducing operational costs and promoting sustainability.
Regulatory Requirements for Data Reporting: Governments introduce regulations mandating building utilities data reporting, driving investment in utilities monitoring and sustainable practices for a greener built environment.